
WORLD FUTURE FUND
http://www.worldfuturefund.org
INTRODUCTION DESCRIPTION CITIZEN
GUIDES READING
LIST SITE INDEX
REPORTS NEWS MULTIMEDIA
SEARCH HOW
TO CONTRIBUTE HELP WANTED
VOLUNTEERS
GRANTS
PUBLICATIONS
PRINCIPLES COPYRIGHT
NOTICE CONTACT
US

DISCLAIMER:
Some people find the beliefs and historical activities of Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab and his followers to be controversial. We're not here to advocate for or disagree with the movement. However, we're providing this information because these ideas continue to be relevant today.
INTRODUCTION
In the 18th century, one man helped set in motion one of the most impactful religious revolutions in history. That man's name was Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab. Ibn Abd al-Wahhab was an Arabian Islamic scholar, theologian, preacher, and activist. He started a movement which claimed to renew the Islamic faith by getting back to basics laid out in the Quran (the holy book of Islam) and Sunnah (the traditions and practices of the Islamic prophet, Muhammad). Ibn Abd al-Wahhab viewed prayers to saints and pilgrimages to their tombs as a form of heresy, idolatry, and innovation.
Ibn Abd al-Wahhab was born into the impoverished Arab clan of Banu Tamim in a village in the Najd region of central Arabia. Yet despite his humble beginnings, his movement would end up spreading to the whole of Saudi Arabia in less than a century, and the movement also survived two major military attempts to crush it.
Ibn Abd al-Wahhab's teachings came to be known as "Wahhabism." However, many people inside this movement don't actually use the term "Wahhabism." Many feel that to call themselves "Wahhabis" is to deify Muhammad Ibn Abd al-Wahhab, which is against the principle of "Tawhid" (the oneness of God). The centrality of Tawhid in the teachings of Ibn Abd al-Wahhab has also led many of his early followers to call themselves “Muwahhidin,” or Unitarians.
His followers have historically done controversial things. Shrines, tombs, and sacred sites associated with early Islamic history were demolished under Saudi rule. However, despite the controversy associated with the movement, there is no denying its global influence today. These teachings have reached Muslims worldwide, from Saudi Arabia, to Nigeria, to Indonesia, to Kosovo, and elsewhere. This movement is backed by the oil wealth of the Saudi kingdom, which is pouring billions into exporting this ideology around the globe. Therefore, we believe it is important to study this movement in order to understand how it has influenced the world, and how it will continue to grow.
Wahhabism (Wikipedia)
The Wahhabi Myth: Debunking the Bogeyman (Muslim Matters, 4-1-07)
Tawhid or Jihad: What Wahhabism Is and Is Not (MEI.edu)
History of Wahhabi Islam (Wikipedia)
Wahhabi History (Britannica)
Wahhabi Islam: From Revival and Reform to Global Jihad (Book on Amazon)
THE KAABA IN SAUDI ARABIA TODAY
ISLAM'S MOST SACRED SITE
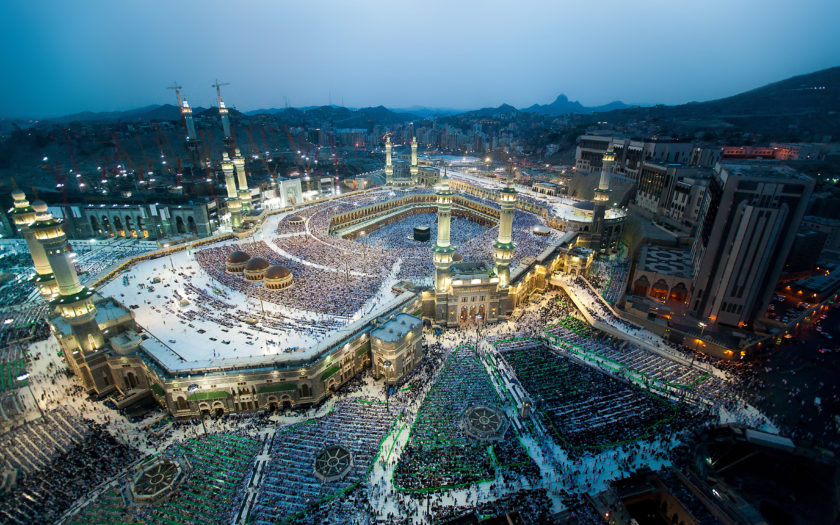

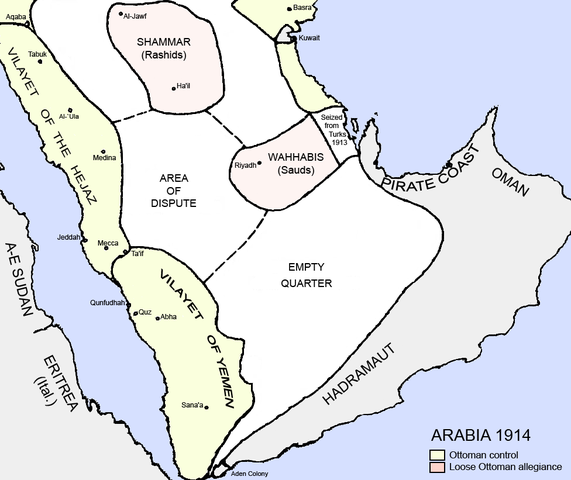
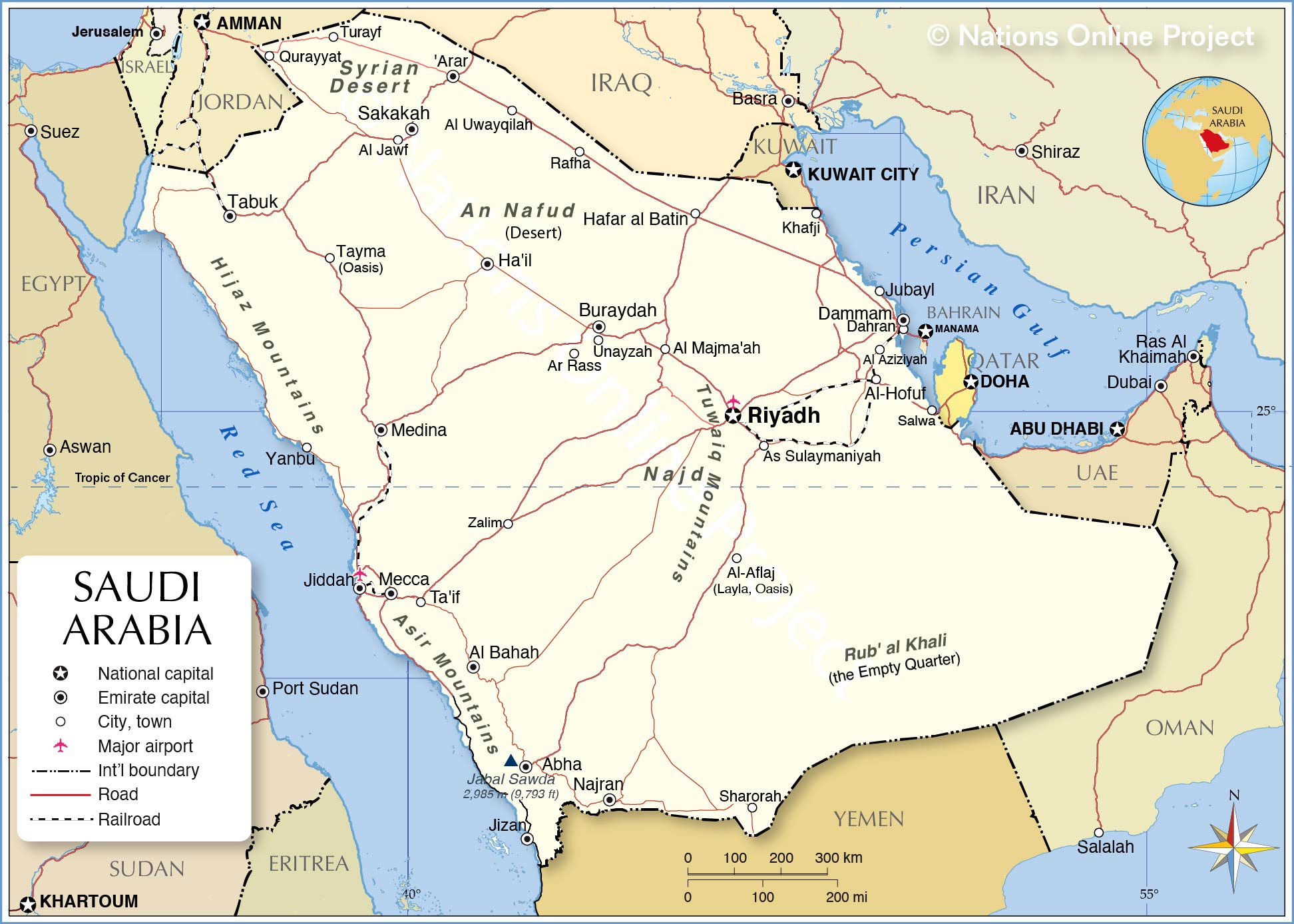
MAP OF THE GROWTH OF THE SAUDI STATE AND WAHHABI REVOLUTION SINCE THE 18TH CENTURY

THE SECOND SAUDI STATE CIRCA 1850
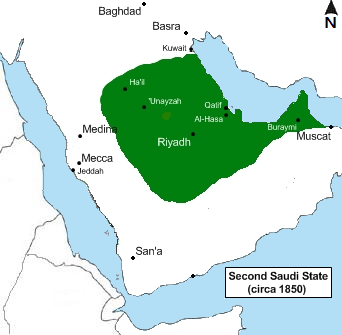
THE THIRD WAHHABI STATE IN 1914
A MAP OF SAUDI ARABIA TODAY
KEY PEOPLE
RELIGIOUS LEADERS
Muhammad Ibn Abd al-Wahhab (Born 1703-Died 1792. In Office from 1744-1773) (Considered to be the founder of the Wahhabi Religious Movement)
Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab (Wikipedia)
A List of Wahhab's Works (Wikipedia)
Muhammad Ibn 'Abd al-Wahhab: The Man and his Works (Library of Middle East History) (Amazon)
Download the Works of Wahhab (Kalamullah) We cannot vouch for the safety of this site as we have not personally downloaded their content ourselves.
Ibn Taymiyya (Born 1263-Died 1328)
Ibn Taymiyya is a 13th century Sunni Islamic scholar.
He has had an influence on several Islamic movements, including the Salafi/Wahhabi movement.
Ibn Taymiyya (Wikipedia)
LEADERS OF THE SAUDI STATES
Muhammad bin Saud Al Muqrin (Born 1687-Died 1765, Ruled from 1727-1765) Founder of the First Saudi State
Muhammad bin Saud was the founder of the Emirate of Diriyah, founder of the first Saudi state and the Saud dynasty. He became the local emir of Diriyah in 1727. Diriyah is where he met Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab, who asked for protection. They formed a historic alliance in 1744. This set in motion the close connection between the Saudi state and the religious Wahhabi movement. Muhammad ibn Abd al-Wahhab's daughter even married Muhammad bin Saud's son. So the descendants of Muhammad bin Saud and Muhammad bin Abdul Wahhab are closely linked.
Muhammad bin Saud initiated a set of attacks against the ruler of Riyadh, but these attacks would last for 28 years, and it was not Muhammad that ended up victorious, but his son, Abdulaziz, who managed to seize Riyadh in 1773.
Muhammad bin Saud Al Muqrin (Wikipedia)
Abdulaziz bin Muhammad Al Saud (Born 1720-Died 1803, Ruled from 1765-1803)
He was nicknamed by his people as the savior of his time (mahdi zamanihi in Arabic) due to what they called his fearless activities and military success. Abdulaziz was also given the titles of both Emir and Imam because of his religious education by Muhammad bin Abdul Wahhab. And during Abdulaziz's reign, Muhammad bin Abdul Wahhab was one of his key advisors.
Abdulaziz led many military campaigns including the capture of Riyadh, upon which it was incorporated into the emirate.
The military victories of Abdulaziz helped spread the influence of Wahhabi teachings.
In 1802, he presided over the sack of Karbala. Karbala is the shrine of Imam Husayn, the grandson of the Prophet Muhammad. Imam Husayn is an important figure for many Shia muslims, who regard him as the third great imam of their twelve infallible imams. The raid was conducted in retaliation against attacks on Hajj caravans by Iraqi tribes.
Abdulaziz bin Muhammad Al Saud (Wikipedia)
Wahhabi sack of Karbala (Wikipedia)
Saud bin Abdulaziz Al Saud (Born 1748 – Died 1814, Ruled from 1803 – 1814)
Saud bin Abdulaziz Al Saud ruled the First Saudi State from 1803 to 1814. It was during this time that Saud annexed Mecca and Medina from the Ottoman Empire, making him the first Al Saud ruler who received the title of The Servant of The Two Holy Cities. During his rule the state experienced a significant level of strength and expansion for which he was called Saud Al Kabeer, or Saud the Great.
Saud bin Abdulaziz Al Saud (Wikipedia)
Abdullah bin Saud Al Saud (Born 1785 - Died 1819, Ruled from 1814-1818)
Abdullah bin Saud Al Saud was the ruler of the First Saudi State from 1814 to 1818. He was the last ruler of the First Saudi State.
At this time, the Saudi state was the target of an invasion by the Ottoman Empire. The Ottoman/Egyptian-Saudi War was fought from early 1811 to 1818, between the Ottoman Empire and the Emirate of Diriyah, the First Saudi State. Eventually, the First Saudi State would get destroyed and Abdullah bin Saud Al Saud would be executed in Constantinople. Although the Ottomans maintained several garrisons in the Nejd thereafter, they were unable to prevent the rise of the Emirate of Nejd, also known as the Second Saudi State, led by Turki bin Abdullah.
Abdullah bin Saud Al Saud (Wikipedia)
Abdulaziz bin Abdul Rahman Al Saud (Born 1876-Died 1953, Ruled From 1902-1953) Founder of Modern Saudi Arabia
Abdulaziz bin Abdul Rahman Al Saud (Known as Ibn Saud in the West) founded the kingdom of Saudi Arabia and reigned as its first king from 1932 until his death in 1953. He used the wealth and influence of the Al Saud house to spread the teachings of Ibn Abd al-Wahhab throughout the newly found kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
Abdulaziz bin Abdul Rahman Al Saud (Wikipedia)
Related World Future Fund Links